See the latest rankings
LAWS & LEGISLATION
The simple and original principle of charter schooling is that charter schools should receive enhanced operational autonomy in exchange for being held strictly accountable for the outcomes they promise to achieve. When charter school laws honor this principle, innovative, academically excellent charter schools flourish. In turn, schools that fail to produce strong outcomes close.
An Introduction to Charter School Laws
Understanding State Charter School Laws: The Building Blocks of Choice
Charter schools, publicly funded but independently operated, owe their existence to state charter school laws. Currently, 47 states and the District of Columbia have enacted these crucial pieces of legislation. These laws, typically initiated and passed at the local or state level, lay the groundwork for the creation and operation of charter schools within their borders.
Why State Laws Matter:
The specifics of a state’s charter school law have a profound impact on the landscape of charter schools within that state. Strong, well-crafted laws, as highlighted by CER, tend to foster a thriving environment for high-quality charter schools, ultimately expanding educational options for families.
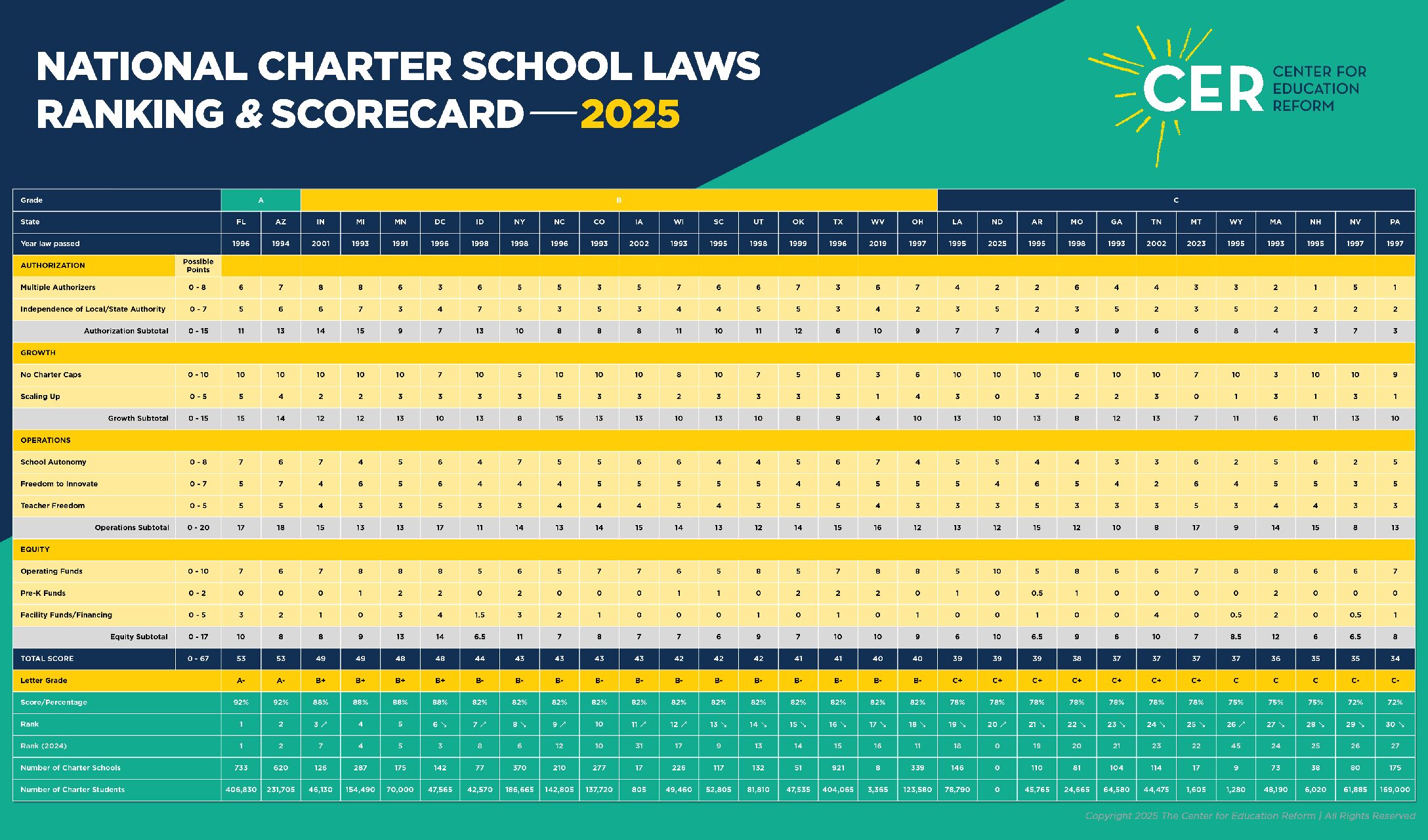
National Charter School Law Rankings & Scorecard—2025:
Since the Center for Education Reform (CER) first began publishing its Charter School Law Rankings in the mid-1990s, it has been at the forefront of evaluating and advocating for policies that strengthen charter school quality and accessibility. From laws that boost accountability and expand access to policies that encourage innovative school models, strong charter school legislation continues to drive real progress in education – and, more importantly, often serves as a powerful launching pad for broader state-level education freedom initiatives. Recent legislative victories reflect this continued investment in education innovation – click here to see the ranks!
One of the reasons parents and students seek charters is because, when they work, they offer options that are distinct from those found in most traditional school districts. The innovations that charters are best known for are extended school days and years and, in some places, one-to-one tutoring. But charters innovate in many other ways as well: from developing unique approaches to teacher training to pioneering tools for personalized learning, many innovations that are now accepted as common were born in the charter sector.
Key Elements of Effective Charter School Laws:
In essence, state charter school laws provide the framework that determines the opportunities and challenges for charter schools, ultimately shaping the educational choices available to families and the potential for innovation within the public education system.
No Limits on Growth
The most effective laws do not cap the number of charter schools allowed to operate or the number of students who can enroll. This encourages the development of diverse school options to meet varying student needs.
Diverse School Types and Applicants
Strong laws enable a wide range of groups to apply to open various types of charter schools (new schools, conversions of existing public schools, online programs, etc.), increasing parental choice.
Multiple Independent Authorizers
Instead of relying on a single entity (like the local school board) for approval, the best laws permit multiple independent organizations to authorize charter schools. This creates more pathways for quality schools to open and can include a fair appeals process for denied applications. Independent authorizers prevent potential conflicts of interest and foster a more diverse and innovative charter school sector.
Operational and Legal Autonomy (Waivers)
Effective laws grant charter schools significant freedom from many traditional school district regulations (excluding fundamental civil rights). This autonomy allows charter schools to innovate in curriculum, staffing, scheduling, and other areas, leading to unique educational models.
Equitable and Full Funding with Fiscal Autonomy
Charter schools, as public schools, should receive the same level of per-pupil funding as traditional public schools, without unwarranted deductions for administrative costs. Furthermore, they need control over their own finances to manage resources effectively and implement their educational vision.
What does a strong charter law look like?
Learn from CER’s 30 years of experience of navigating charter school legislation in our seminal publications and research.

Charter Authorizing: The Truth about State Commissions
State charter school law debates have taken a dicey turn, necessitating a reevaluation by lawmakers and advocates.

The Essential Guide to Charter School Lawmaking: Model Legislation for States
CER’s roadmap for charter school law focuses on Independent and Multiple Authorizers, Number of Schools Allowed, Operations, and Quality. This framework, developed from 20 years of experience, reflects effective and ineffective policies.
HERE’S WHY WE FIGHT FOR CHARTER SCHOOLS.
Award-winning charter schools recognized for their sustainability, transformational impact, outstanding performance, and permissionless models are showcased below.


Charter schools are popular and innovative. They are also effective. But charter school success depends on the policy environments in which charter schools operate. Some state laws and regulations encourage diversity and innovation in the charter sector by providing multiple authorizers to support charter schools and allowing charters real operational autonomy. As Michael Q. McShane has pointed out, where diversity exists, charter schools have the opportunity to innovate.
Too many states, however, hamper charter schools with weak laws and needless regulations. These make it difficult to distinguish charters from their district counterparts.
Weak charter school laws have proven that when we apply the same old rules to district and charter schools, we get more of the same. Overregulation and underfunding force charters to behave as district schools by another name. Wouldn’t it make more sense to allow charters the room to innovate and succeed so that they could, in turn, help district schools subvert the status quo?
Since 1996 CER has researched, analyzed and ranked state charter school laws in an attempt to demonstrate how weak charter school laws create weak charter schools. These findings consider not only the content of each law, but also how the law impacts charter schools on the ground: How robust is the charter sector in each state? How diverse are the schools? To what extent do burdensome regulations prevent charters from doing anything meaningfully different?
Review Prior Law Rankings to Learn about the progress we’ve made
National Charter School Laws Across the States Ranking & Scorecard
Established in the 1990s, charter schools have expanded nationwide, particularly in urban areas, facing demand despite policy issues and opposition. Parents and students choose charters for their distinct options and innovations like extended school time and personalized learning, which have influenced traditional education.
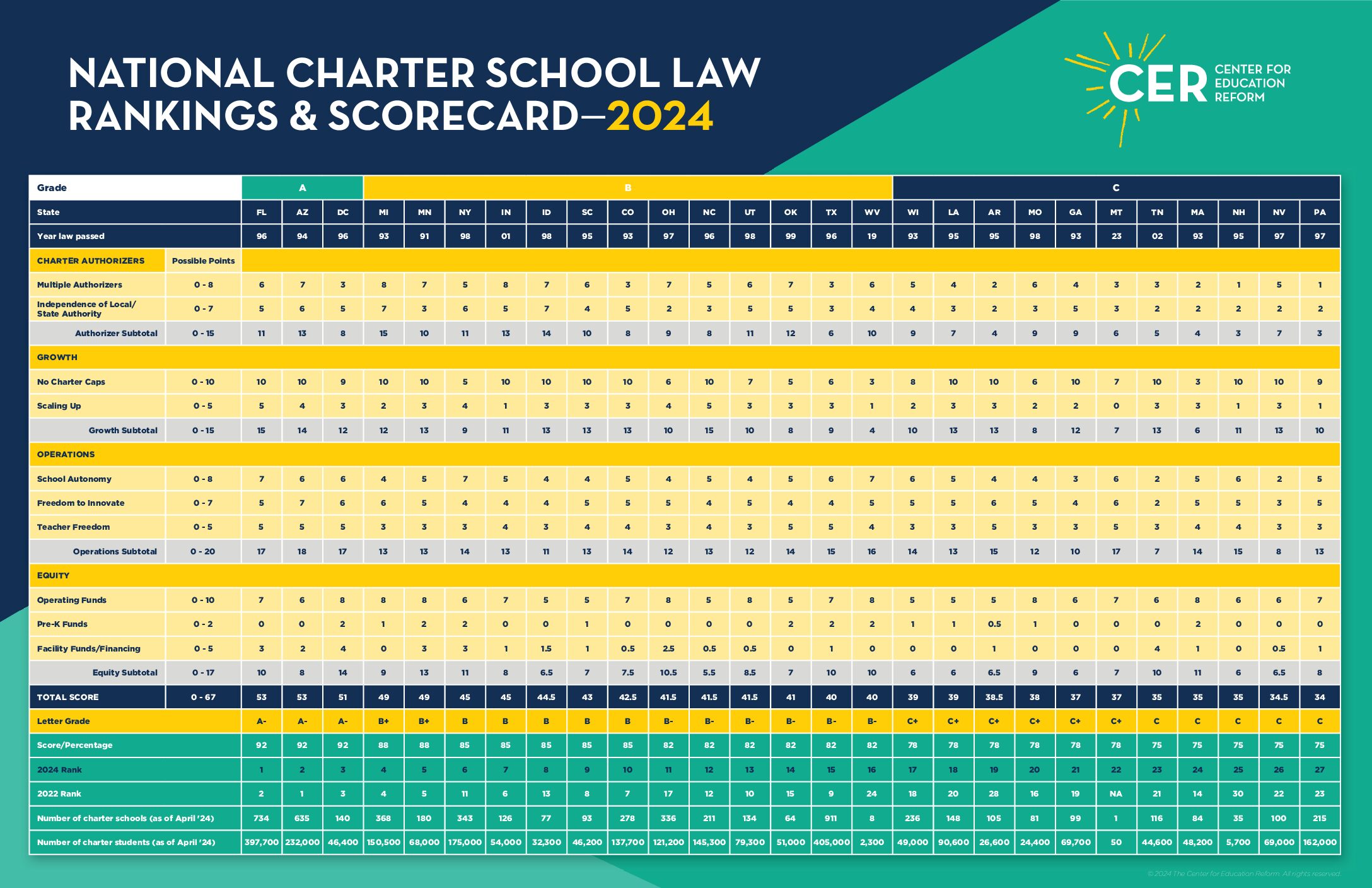
CLICK HERE TO VIEW THE 2024 NATIONAL CHARTER SCHOOL RANKINGS
The simple and original principle of charter schooling is that charter schools should receive enhanced operational autonomy in exchange for being held strictly accountable for the outcomes they promise to achieve. When charter school laws honor this principle, innovative, academically excellent charter schools flourish. In turn, schools that fail to produce strong outcomes close.
CLICK HERE TO VIEW THE 2022 NATIONAL CHARTER SCHOOL RANKINGS
As in years past, the national rankings carefully consider the impacts of overregulation, particularly on innovations in teaching and learning. And this year’s National Charter School Law Rankings & Scorecard goes a step further, providing case study examples of how regulations and other aspects of poorly conceived charter school policies impact charter operators and students. In addition to these case studies, CER also provides model legislation for policymakers to consider when crafting or amending charter school laws and regulations.
With this important guide, there is evidence-rich feedback and guidance to policymakers. With feedback and guidance, change is possible.
CLICK HERE TO VIEW THE 2021 NATIONAL CHARTER SCHOOL RANKINGS
As in years past, the national rankings carefully consider the impacts of overregulation, particularly on innovations in teaching and learning. And this year’s National Charter School Law Rankings & Scorecard goes a step further, providing case study examples of how regulations and other aspects of poorly conceived charter school policies impact charter operators and students. In addition to these case studies, CER also provides model legislation for policymakers to consider when crafting or amending charter school laws and regulations.
With this important guide, there is evidence-rich feedback and guidance to policymakers. With feedback and guidance, change is possible.
CLICK HERE TO VIEW THE 2018 NATIONAL CHARTER SCHOOL RANKINGS
We are now well into the third decade since Minnesota passed the first state charter statute. The number of charter schools has continued to increase each year at a steady but relatively slow pace. But this past year, that growth abruptly came to a near halt. Overall, the nation’s nearly 7,000 charter schools still serve a fairly small percentage of the total number of students receiving public education, roughly six percent. Some states and cities have far more market share and point the way to what healthy expansive choice does for the whole of public education.
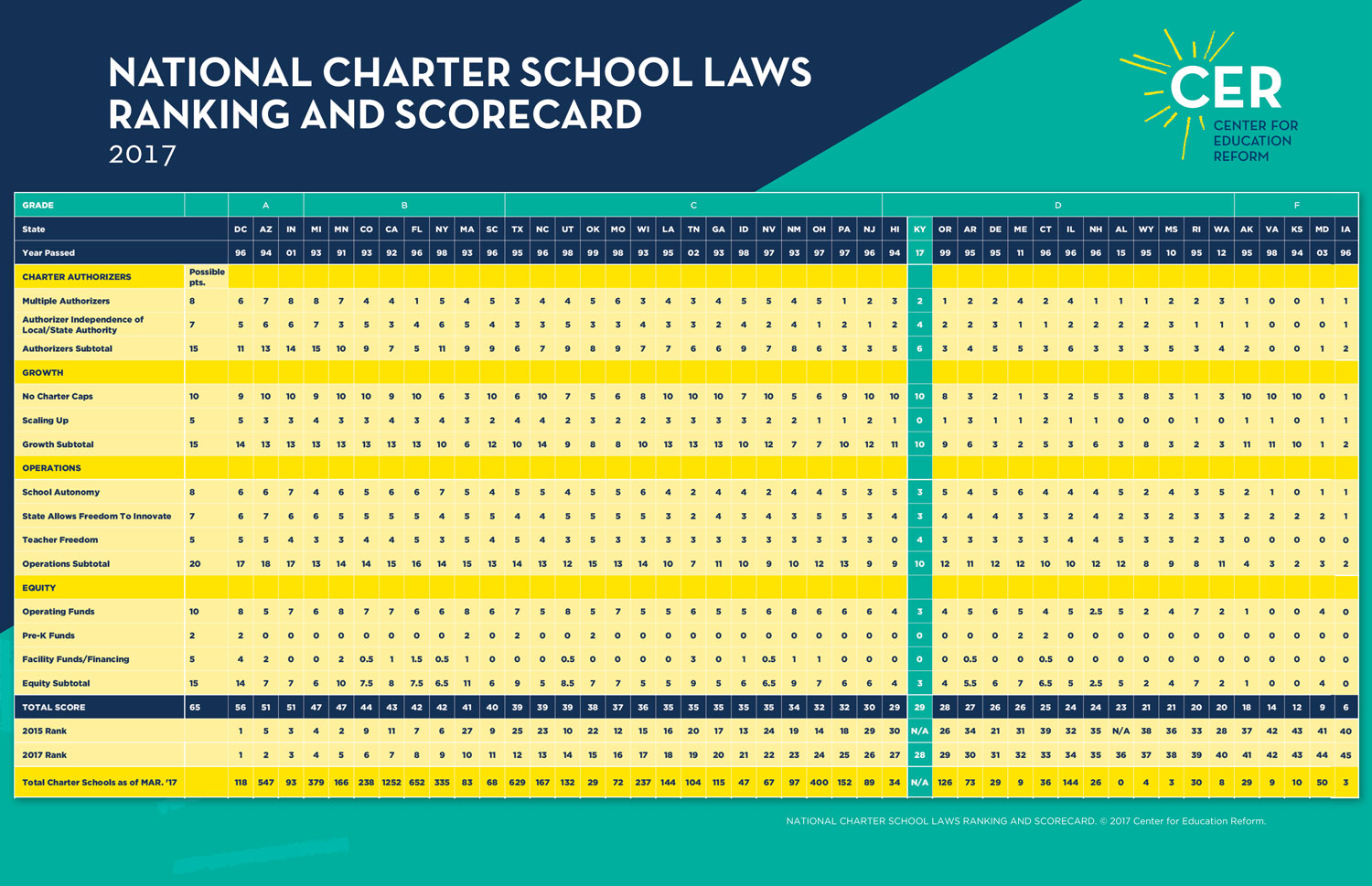
CLICK HERE TO VIEW THE 2017 NATIONAL CHARTER SCHOOL RANKINGS
Charter School Law Rankings: Read CER’s 16th edition of Charter School Laws Across the States 2015 Rankings & Scorecard here.
“It is abundantly clear that little to no progress has been made over the past year. Charter school growth does continue at a steady, nearly linear pace nationally, especially in states with charter laws graded ‘A’ or ‘B,’ but an even more accelerated pace would allow charter schools to play a more central role in addressing the demands and needs of our nation’s students.” Read More.
Compare how states stacked up previously with the 15th edition of Charter School Law Rankings.
Which states have strong charter school laws?
Understanding Charter School Laws and How They Are Ranked:
Clarifying what you need to know for effective policymaking by pointing out how state policy reports differ from one another.
Every year, the Center for Education Reform rates state charter school policy based on four major components that determine the development and creation of high-quality, autonomous charter schools:
1.
The existence of independent and/or multiple authorizers2.
The number of schools allowed and state caps3.
Operational and fiscal autonomy4.
Equitable funding
For more on these components, visit Charter School Law Rankings & Scorecard: The Rationale Behind the Rankings.
Get the latest Charter School Laws Across the States Rankings and Scorecard here.